Describe the Structure of the Bladder
When empty the bladder is about the size and shape of a pear. The size and shape of the.

Urine Transport And Other Structures Of The Urinary System Anatomy And Physiology
1-3 The inside of the bladder is lined with a thin layer of cells.
. Unlike the mucosa of other hollow. It is thought to prevent. The urethra is a hollow tube positioned between the urinary bladder and urinary meatus which takes urine stored in the bladder out of the body.
Male consists of circular smooth fibres which are under autonomic control. The urinary bladder is made of several distinct tissue layers. The empty bladder is about the size and shape of a pear.
The male urethra is divided into three parts. The bladder divideS into two main parts each with its own features. The mucosa lining the urinary bladder is additionally.
The prostatic urethra membranous urethra and the spongy urethra. This triangle-shaped hollow organ is located in the lower abdomen. Mucosa layer forms the innermost layer lining the hollow organ.
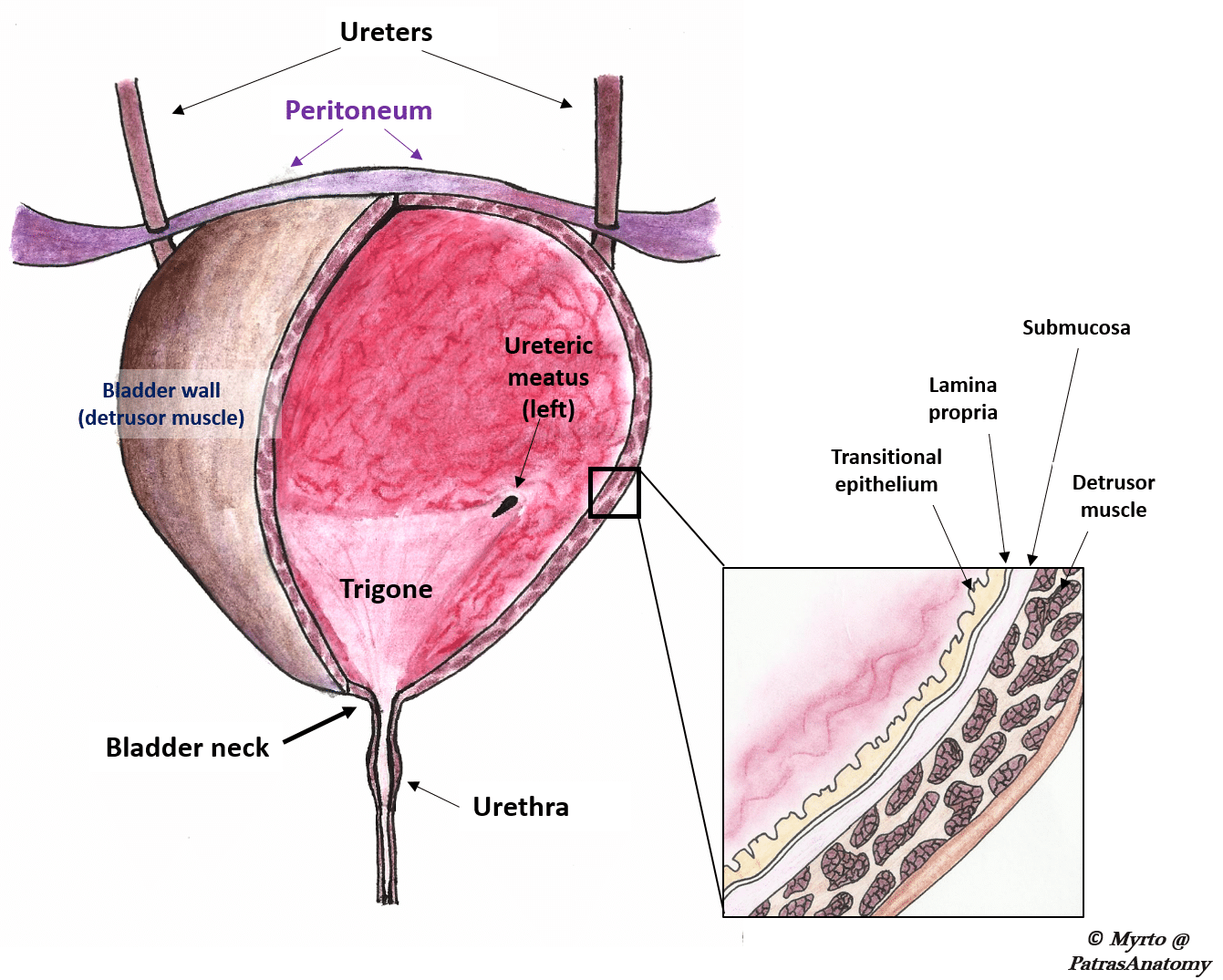
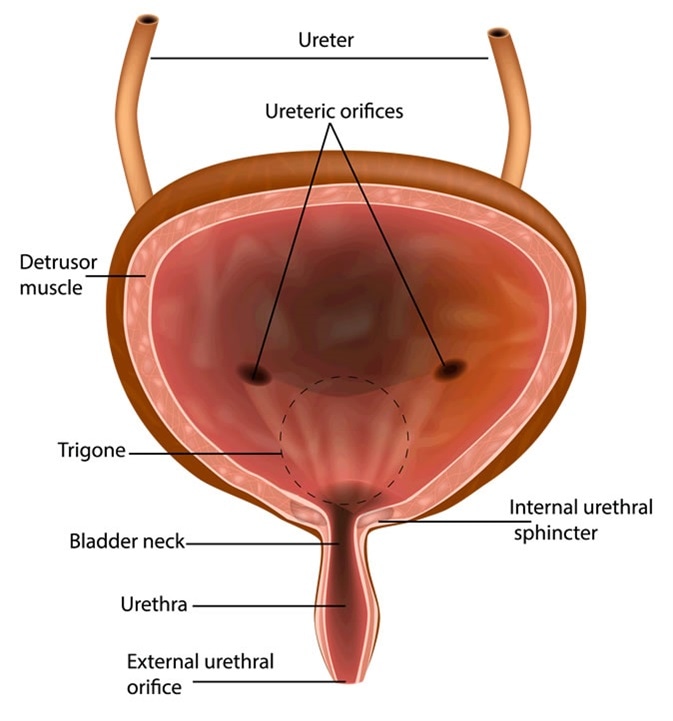
What are the basic layers that form the structure of the urinary bladder. The upper part above the ureteric orifices is composed of the apex and body while the lower part is. The urethra enters at the trigone of the bladder.
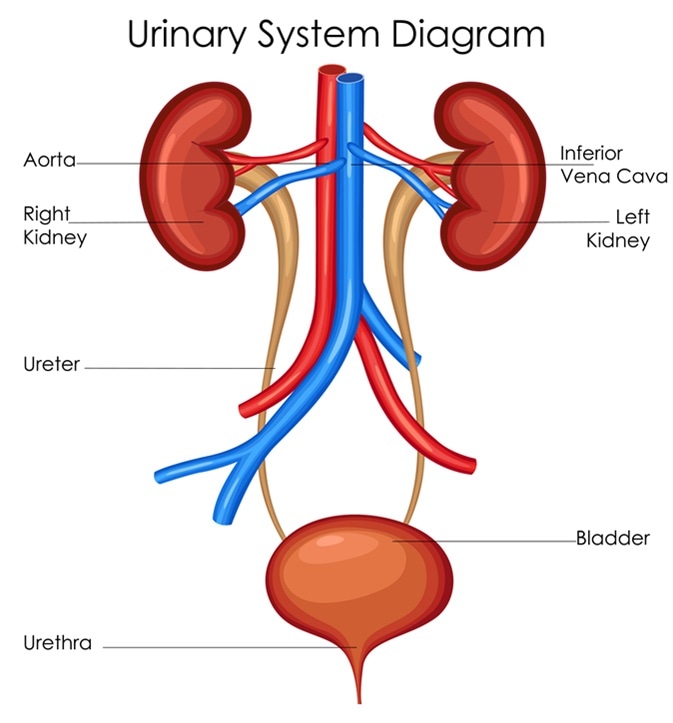
Modification of work by NCI The kidneys illustrated in Figure 1 are a pair. Urine drains from the kidneys into the bladder through the ureters. The bladder is partially retroperitoneal with its peritoneal-covered dome projecting into the abdomen when the bladder is distended with urine Figure 3.
Within the base of the bladder is a structure known as a trigone. Generally the bladder is a hollow muscular and pear-shaped distensible elastic organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Kidneys filter the blood producing urine that is stored in the bladder prior to elimination through the urethra.
The trigone of the urinary bladder is formed by the two. It is located in the pelvic cavity posterior to the symphysis pubis and below the parietal peritoneum. Anatomy of the Bladder.
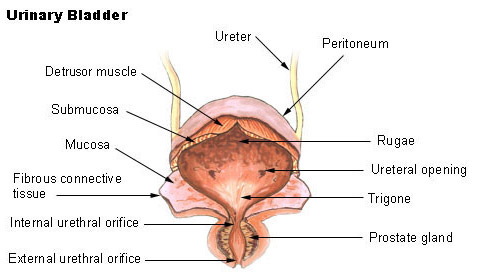
The bladder like the stomach is an expandable saclike organ that contracts when it is empty. The bladder walls are mainly made up of muscle tissue but the inside of the bladder is lined with two different types of tissue. The urinary bladder consists of different layers of tissue.
The fundus of the bladder contains three openings which form the trigone of the bladder. One for each ureter. The prostatic urethra starts at the neck of the bladder and is.
The innermost layer of the bladder is the mucosa layer that lines the hollow lumen. 1Mucosanumerous folds 2Muscular layer has 3 distinctives layers of smooth muscle. The urinary bladder is a temporary storage reservoir for urine.
The bladder contains three openings or orifices. It is formed by the anatomy of the bladder neck and proximal urethra. How the Structures of the Urinary System Work 1.
The bladder is the holding reservoir for urine until urination. The bladders walls relax and. It is located in the lower pelvic cavity.
The urethra is the. The inferior portion of the. The inner lining of the bladder tucks into the folds and expands out.
It receives urine via the ureters which are. The trigone is the triangular area made up of the openings from the ureters and the opening into the urethra. The urinary bladder is a muscular sac in the pelvis just above and behind the pubic bone.
Kidneys Filter Blood at the Top of the Urinary System The kidneys are bean-shaped organs situated on the. Filtering Blood Removing Urine. It contains the trigone which is.
Urethra length differs in. It is held in place by ligaments that are attached to other organs and the pelvic bones.
The Urinary Bladder Structure Function Nerves Teachmeanatomy
Comments
Post a Comment